The tomb of Senenmut, an influential figure during the reign of Pharaoh Hatshepsut, stands as a remarkable testament to the sophistication of ancient Egyptian astronomy. Nestled in Deir el-Bahri near Luxor, this tomb is celebrated for its pioneering depictions of celestial phenomena, blending scientific observation with religious and cultural significance.
The Role of Senenmut and His Tomb
Senenmut, a trusted official, and architect of the 18th Dynasty, played a crucial role in the reign of Hatshepsut. Beyond his administrative achievements, his tomb reflects a profound connection between the cosmos and ancient Egyptian spirituality.
The astronomical ceiling within the tomb demonstrates a deliberate effort to capture the Egyptians’ understanding of the heavens, a subject critical to their daily lives, religious practices, and governance.
Depictions of Constellations and Star Clusters
One of the most striking elements of the tomb is its depiction of constellations and star clusters.
- Analysis: These depictions not only highlight the Egyptians’ observational skills but also emphasize their reliance on the stars for practical purposes like navigation and timekeeping. Specific constellations likely held mythological importance, representing gods or protective deities.
- Significance: This suggests a dual purpose—astronomical records for daily use and symbols of divine order, reinforcing the Egyptians’ belief in Ma’at (cosmic harmony).
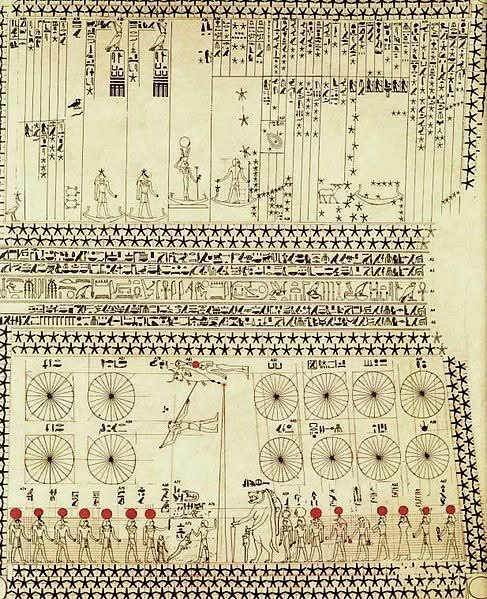
The Celestial Boats and Their Symbolism
Another notable feature of the tomb is the representation of celestial boats, carrying gods across the sky.
- Analysis: The journey of these boats, particularly the one carrying the sun god Ra, mirrors the solar cycle and represents themes of life, death, and rebirth. This imagery tied the movement of celestial bodies to the human experience of mortality and the promise of the afterlife.
- Significance: These depictions served as metaphors for the renewal of life and cosmic balance, reassuring viewers of the universe’s unchanging rhythms.
Astronomical Diagrams and Practical Applications
The tomb’s ceiling also features detailed diagrams of celestial movements, including the sun, moon, and planets.
- Analysis: These diagrams reflect the Egyptians’ sophisticated efforts to track and predict astronomical events. For instance, the heliacal rising of Sirius marked the annual flooding of the Nile, critical for agriculture.
- Significance: By aligning their calendar and festivals with celestial events, the Egyptians integrated their understanding of astronomy into every aspect of life, from food production to religious celebrations.

Broader Cultural and Scientific Impact
The astronomical depictions in Senenmut’s tomb demonstrate the Egyptians’ ability to combine observation with symbolic meaning.
- Art and Science: The ceiling represents a rare blend of precise astronomical knowledge and artistic expression.
- Legacy: These depictions provide modern scholars with invaluable insights into how ancient Egyptians perceived and interpreted the cosmos, revealing a culture deeply attuned to the natural world.
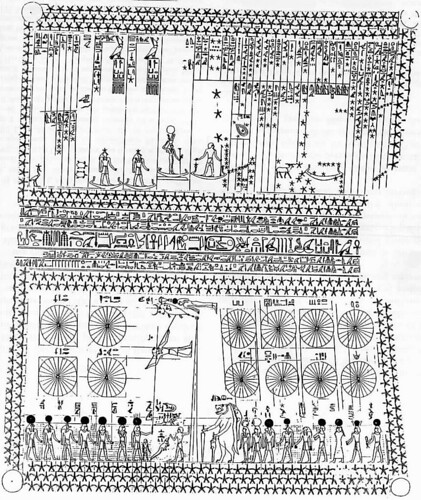
Conclusion
The astronomical depictions in Senenmut’s tomb exemplify the advanced scientific knowledge and spiritual richness of ancient Egypt. By immortalizing their understanding of the heavens in art, the Egyptians created a lasting legacy that continues to inspire awe and admiration. Senenmut’s tomb is not just a burial site but a celestial archive, bridging the earthly and the divine.

