Within the British Museum lies a remarkable artifact—the sarcophagus of Vizier Sasobek, a high-ranking official during the reign of Pharaoh Psamtik I, which showcases the artistry and beliefs of the 26th Dynasty of ancient Egypt. This sarcophagus, crafted from black siltstone, is believed to have originated from Sais, the ancestral city of Psamtik’s family. Its anthropoid design represents the pinnacle of Late Period funerary art.
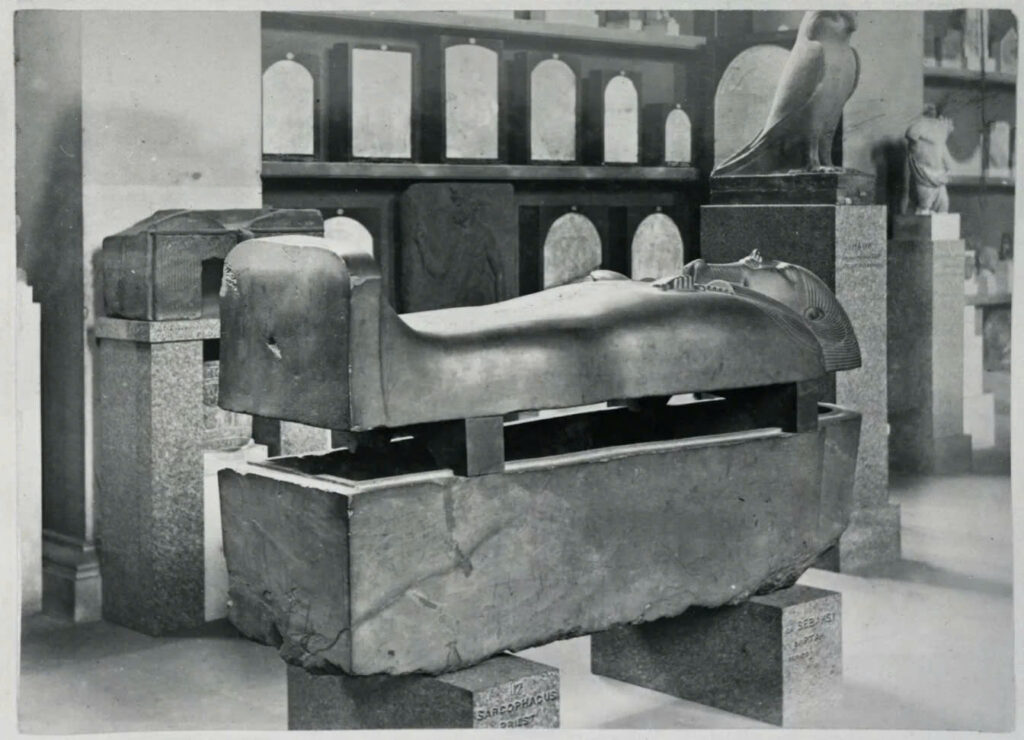
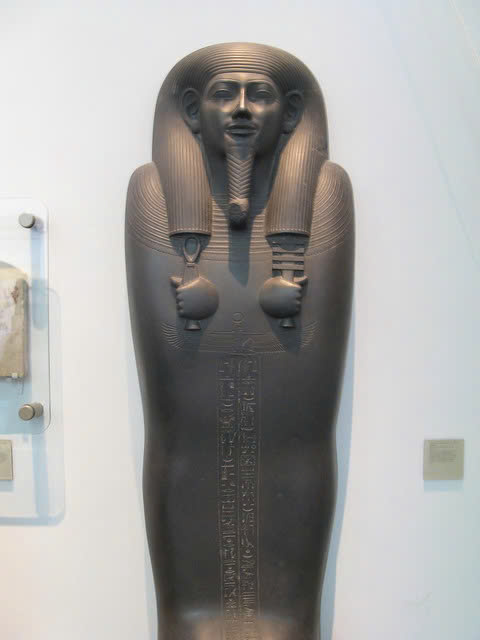
What distinguishes this sarcophagus is its exceptional preservation and the naturalistic rendering of Sasobek’s features. Unlike many anthropoid sarcophagi that display exaggerated characteristics, Sasobek’s visage exudes serenity and lifelike qualities. In his hands, he holds powerful symbols of Egyptian mythology: the djed pillar representing Osiris, the god of the afterlife, and the tyet knot associated with Isis, the embodiment of motherhood and protection.

The tradition of using stone sarcophagi dates back to the dawn of the Old Kingdom (around 2613 BC), but the concept of human-shaped containers for the deceased only emerged during the Middle Kingdom. Currently, Sasobek’s sarcophagus, designated as EA17, continues to captivate visitors and scholars alike, reflecting the skill of ancient Egyptian artisans and providing valuable insights into the funerary practices of a civilization that remains fascinating to us today.
Video

