The recent excavations within the hallowed halls of Paris’s Notre Dame Cathedral have unearthed a remarkable discovery – the remains of a knight with an elongated skull, interred at the most sacred site in medieval France. This unexpected find has captivated the world, shedding light on the intriguing history and hidden secrets that lie beneath the iconic cathedral.
The foundation stone of Notre Dame Cathedral was laid by Pope Alexander III in 1163 AD, and the structure has stood as a symbol of the city’s rich history for centuries. However, the disastrous fire of 2019 nearly destroyed this architectural masterpiece, leaving the world anxiously awaiting its restoration.
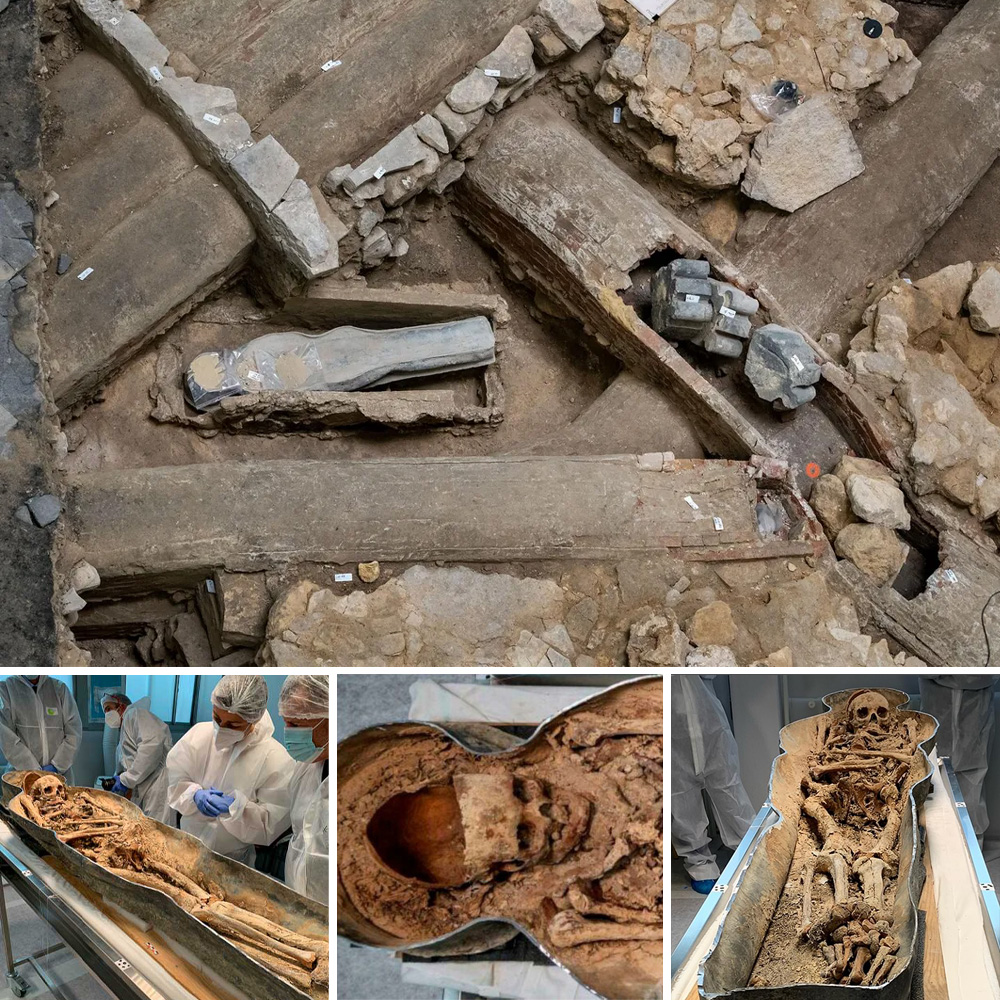
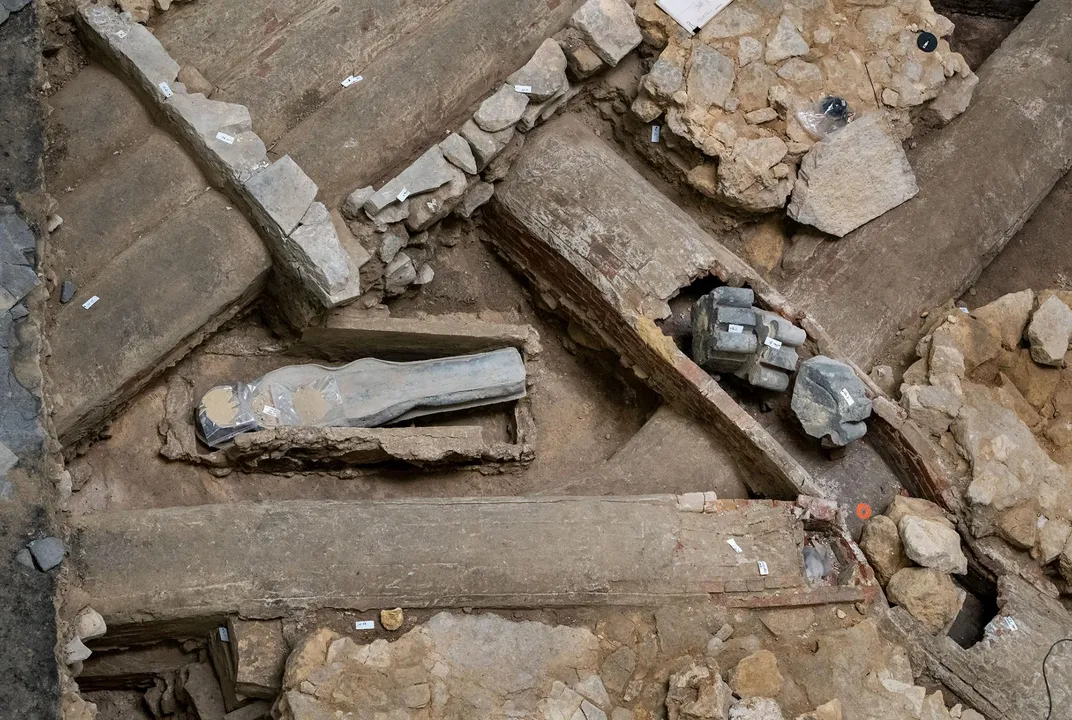
As the reconstruction efforts progressed, archaeologists began excavating the area beneath the cathedral’s transept, where the nave and choir intersect. It was here, in this holiest of spaces, that they made a startling discovery – two well-preserved lead sarcophagi, along with numerous fragments of statues and religious relics.
The Enigmatic Knight with an Elongated Skull
The first sarcophagus was found to contain the remains of a high-ranking canon of the cathedral, identified as Antoine de la Porte, who had died in 1710 at the age of 83. The second coffin, however, held an even more intriguing find – the remains of a young knight, estimated to have been in his thirties.
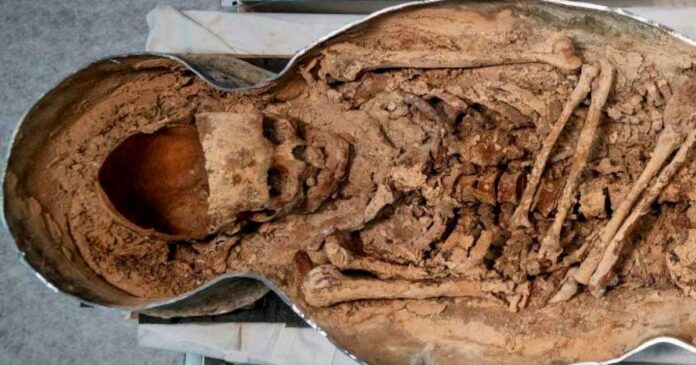
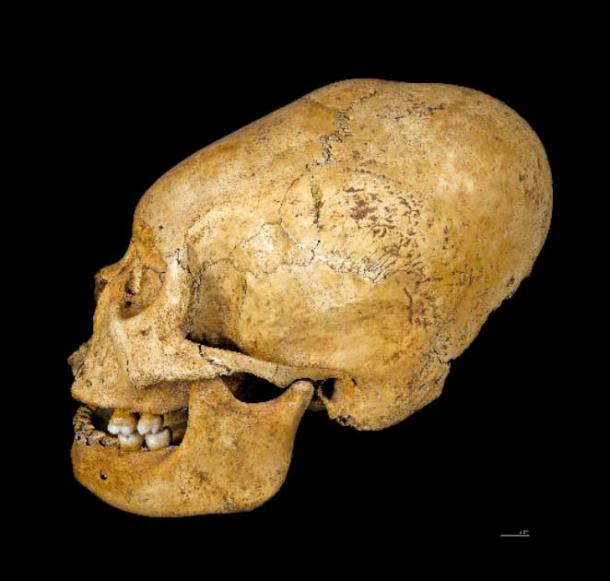
What made this discovery particularly remarkable was the knight’s unusual physical feature – an elongated skull. This skull deformation, known as cranial modification, was a practice associated with certain elite and privileged groups in medieval Europe.
The researchers speculate that this knight was of the upper echelons of the 14th century French aristocracy, as evidenced not only by his skull shape but also by the fact that he was buried in such a prestigious location within the cathedral. Additionally, the discovery of embalming materials and a crown of flowers further suggests that this individual held a position of great importance and status.
Uncovering the Significance of the Burials
The placement of these burials at the heart of the Notre Dame Cathedral, directly beneath the former rood screen that separated the clergy from the congregation, underscores the significance of the individuals laid to rest there. Eric Crubézy, a professor of biological anthropology, notes that these men were “clearly important in their respective eras to have been buried in such prestigious tombs at the heart of the cathedral.”
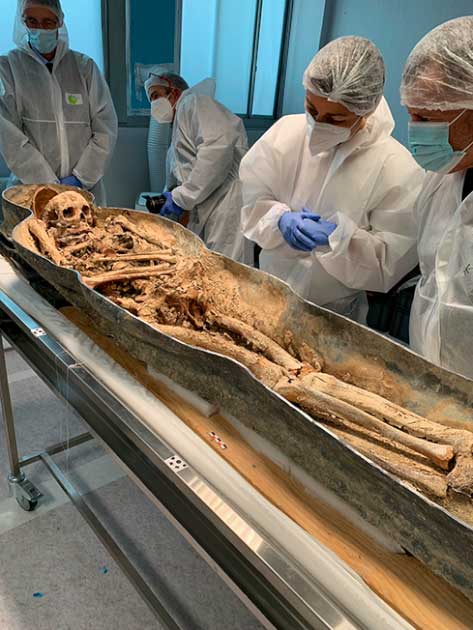
The discovery of the canon’s brass plaque and the knight’s embalmed remains offer valuable insights into the religious and social dynamics of the time. The canon’s position of influence and wealth, as evidenced by his commissioned works of art, provides a glimpse into the power and privilege held by the clergy within the medieval Church. Meanwhile, the knight’s elite status and privileged burial location suggest a complex social hierarchy that extended even into the sacred spaces of the cathedral.
Implications and Significance of the Findings
The unearthing of these remarkable burials within the Notre Dame Cathedral has captured the imagination of scholars and the public alike. This discovery not only sheds light on the cathedral’s long and storied past but also raises intriguing questions about the social and religious structures of medieval France.

The presence of the enigmatic knight with the elongated skull, in particular, poses fascinating questions about the practices and beliefs of the French elite during that era. The skull deformation, a deliberate and culturally significant modification, suggests a connection to the privileged classes and potentially even to mystical or spiritual traditions.
Conclusion
The recent excavations at Notre Dame Cathedral have revealed a treasure trove of historical artifacts and the remains of two intriguing individuals, one a high-ranking canon and the other a young knight with an elongated skull. These discoveries offer a tantalizing glimpse into the complex social and religious dynamics of medieval France, and they continue to captivate scholars and the public alike.
As the restoration of Notre Dame progresses, the insights gained from these findings will undoubtedly play a vital role in our understanding of the cathedral’s rich history and its enduring significance within the fabric of French and European culture. The secrets of the past continue to unfold, inviting us to explore the mysteries that lie within the hallowed walls of this iconic Parisian landmark.

