Writing is traditionally regarded as one of the cornerstones of civilization. Various writing systems have emerged throughout history, with alphabetic writing being one of the most influential. This system is characterized by a standardized set of letters representing basic sounds, or phonemes, of a spoken language. Examples of alphabetic writing systems include the Latin alphabet, the Arabic alphabet, and the Cyrillic alphabet. But how did this system come into existence, and what were its precursors?
Before the Alphabet
Despite the importance of the alphabet today, it did not exist from the very beginning of recorded history. In Mesopotamia, considered the cradle of civilization, the cuneiform script was developed by the Sumerians around the end of the 4th millennium BC. This writing system predates the alphabet by over a millennium, highlighting the alphabet’s relatively recent advent.

The origins of the alphabet can be traced back to ancient Egypt. However, it is important to note that the ancient Egyptians themselves did not create the alphabet. Instead, they used hieroglyphs, a system that included both logograms (symbols representing whole words) and phonetic elements.
The Place of Hieroglyphics
The earliest alphabetic systems are thought to have been inspired by Egyptian hieroglyphics. One such early script, known as Proto-Sinaitic, is believed to have been developed either during the 19th century BC by Canaanite workers in the Sinai Peninsula or during the 15th century BC by Semitic workers in Central Egypt. Proto-Sinaitic is considered a precursor to the alphabetic writing systems that followed.
Antecedents to the Modern Alphabet
Proto-Sinaitic was not the only early script; another significant one was the Ugaritic script. Discovered on approximately 5000 clay tablets in Ugarit (modern-day Syria), this script is thought to have been created between the 14th and 12th centuries BC. The Ugaritic script featured 27 consonants and 3 vowels and was written from left to right, much like modern English.
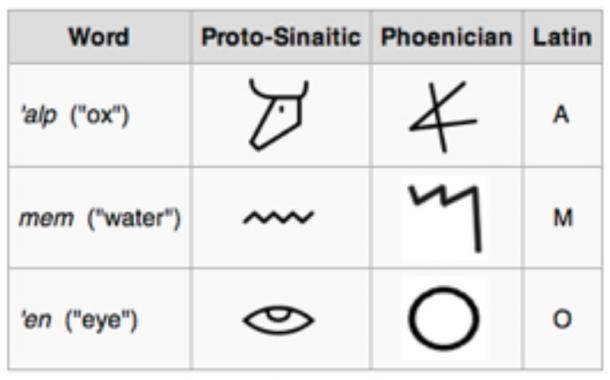
Though Proto-Sinaitic had a significant role in the development of the alphabet, the Ugaritic script was also influential. Scholars hypothesize that the Phoenician alphabet, which is closely linked to the Proto-Sinaitic script, emerged from this earlier system. However, since Proto-Sinaitic has not been fully deciphered, these connections remain speculative.
From the Phoenicians to the Greeks

The evolution of the alphabet becomes clearer with the Phoenician script. By the 8th century BC, the Greeks adopted and adapted the Phoenician script to their own language, creating what is known as the Greek alphabet. The term “phoïnikeia grammata” (meaning ‘Phoenician letters’) reflects the Greeks’ acknowledgment of the script’s origins. This adoption illustrates the interconnectedness of Mediterranean cultures during this period.
Spread Through Conquest

The alphabet’s influence expanded further during the 5th century BC when the Latins, an Italic tribe, encountered Greek colonies and the Etruscans, both of whom used alphabetic scripts. The Latins adapted the Greek alphabetic system, which eventually contributed to the development of the Latin alphabet. As the Roman Empire grew and conquered much of Europe, the Latin alphabet spread throughout their vast empire, leaving a lasting legacy on modern written languages.
Conclusion
From its early beginnings in ancient Egypt to its spread across the Mediterranean and beyond, the evolution of the alphabet is a testament to the interconnectedness of ancient civilizations. The alphabetic writing system we use today has deep roots in the writing systems that came before it, reflecting a rich history of adaptation and cultural exchange. Understanding this history not only illuminates our past but also underscores the enduring impact of these early writing systems on modern civilization.

